The Unemployment Rate among European Young People: A Persistent Challenge

Photo: Unsplash.com

Photo: Unsplash.com

In the realm of entrepreneurial success stories, few are as remarkable as the tale of the Paval brothers, Adrian and Dragos. With unwavering determination, sheer hard work, and an unyielding vision, they transformed their humble beginnings into a thriving business empire

The Peruvian President, Dina Boluarte, on Thursday called for dialogue to end the demonstrations that are shaking several regions of this country, where protesters are demanding her resignation.

After half a century since humanity last touched the lunar surface with the Apollo missions, the United States is poised to make history yet again.

The Industrial Revolution marked the turning point when greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions started to exponentially increase. A new paradigm of production and consumption emerged as a result of the increasing global population

SAN SALVADOR, El Salvador – Nayib Bukele, the charismatic and controversial leader of El Salvador, proclaimed a resounding victory in the nation’s presidential elections.

Wildfires fueled by extreme heat and high wind spread further across California, Oregon, and Washington on Thursday, destroying hundreds of homes and killing at least seven people.

In the heart of Europe, the political landscape is once again shifting. Slovakia, a nation of 5.5 million people, is preparing for another pivotal moment in its political history.
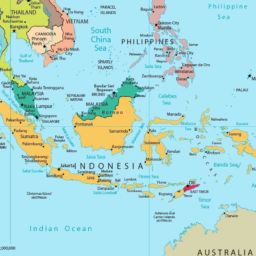
Southeast Asia is quickly emerging as the Asian epicenter of the United States-China great power competition.

In the contemporary political landscape, Russia has often been characterized as a state where democratic values and principles have been markedly absent.

How many people do not experience any symptoms after becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2? And what is their role in spreading COVID-19?

As of August 2023, the Republic of Haiti remains embroiled in a complex web of political and economic challenges.

Recently, Germany discussed a plan to address a spending reduction issue of up to 600 billion euros, exacerbating industry concerns about the fiscal and debt risks of the European Union.

The assassination of Muammar Gaddafi, the former leader of Libya, remains a subject of intense controversy and speculation. Gaddafi’s ousting in 2011 during the Libyan Civil War.

The 37th Harbin International Ice and Snow Sculpture Festival in China have opened to visitors, featuring frozen towers, palaces and castles.

Lithuania has formally protested against the statements made by Belarusian President Aleksandr Lukashenko that hinted at potential military operations against the neighboring country.

